Dr. Seemal Desai presented information about vitiligo and provided updates about emerging treatment options. Vitiligo is a chronic autoimmune disease that targets melanocytes, causing skin depigmentation. Its pathogenesis is largely regulated by interferon-γ activation of the Janus kinase (JAK) signaling pathway.
First, Desai described treatment options for vitiligo, including topical and systemic therapies, phototherapy, depigmentation therapy, surgical procedures, and psychological therapy. He suggested dosing strategies for systemic steroids and presented evidence for antioxidants as part of the treatment regimen. Twice weekly tacrolimus can reduce the relapse rate from 40% to 10% within one year of stopping treatment. Desai noted that 70% to 80% of face lesions can achieve complete or almost-complete repigmentation.
Second, Desai shared data from clinical trials investigating the use of oral and topical JAK inhibitors for vitiligo. The cream formulation of ruxolitinib, a JAK1/2 inhibitor, showed substantial repigmentation in a 52-week phase 3, dose-ranging, randomized study in adult patients with vitiligo. Dr. Desai discussed results from two phase 3 trials of ruxolitinib cream after 52 and 104 weeks of treatment. Many participants showed continuous improvement through week 104. In addition, Desai reviewed several clinical trials evaluating oral JAK inhibitors for vitiligo, including upadacitinib, povorcitinib, and ritlecitinib.
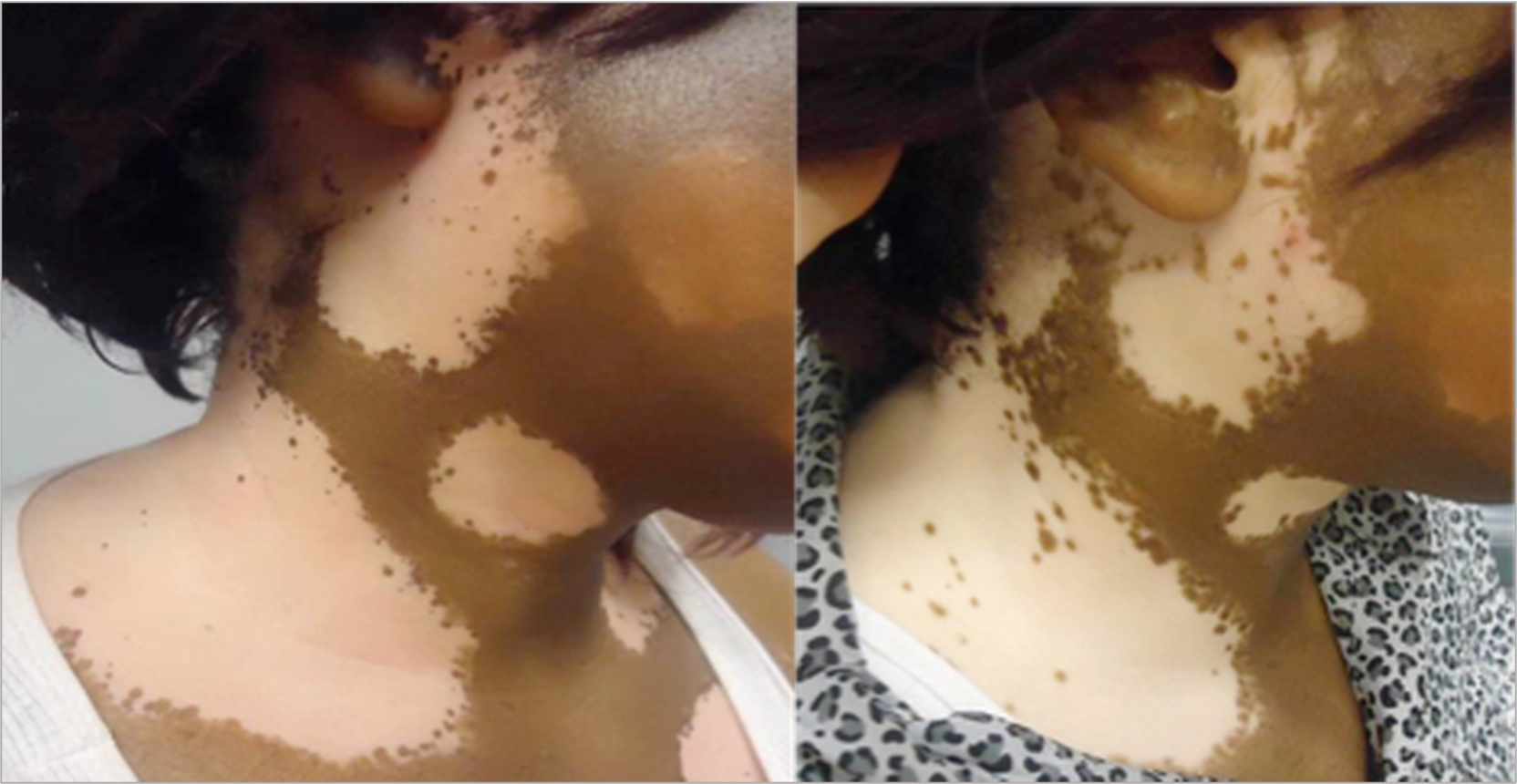
Before and after image of Black woman with skin depigmentation.
To conclude, Desai discussed the RECELL system, a surgical procedure recently approved by the FDA for stable vitiligo lesions after first-line therapies for repigmentation were not efficacious. The RECELL system allows for the point-of-care preparation of a non-cultured autologous skin cell suspension containing melanocytes. It does not require specialized skills or equipment, and it has a donor-to-treatment site expansion ratio of 1:20. To perform the procedure, the clinician takes a skin sample from a pigmented skin area and uses the RECELL device to create a cell suspension. The recipient site is prepared for the procedure using laser ablation to remove the epidermis. The cell suspension is dripped over the recipient site and covered with dressings. This procedure can offer effective, durable repigmentation after 52 weeks.
Mark January 28-31, 2026, on your calendar for the 2026 Annual DF Clinical Symposium.

